What a periodontist treats and what symptoms to see a periodontist for
Among dentists, there are quite a few narrow specialists whose names are not always clear to ordinary people. A periodontist is one of these specialists. What does he treat, with what symptoms to address him and what methods he uses in his practice? We will tell you more about it right now.
What diseases are treated by a periodontist
A periodontist treats the periodontal tissues that surround the tooth. This includes the gums, ligaments, bones, where there are vessels and nerves that feed and supply blood to the tooth row. The following diseases are most often encountered by the specialist:
- Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums and surrounding tissues.
- Periodontitis is the spread of the process to deeper periodontal tissues.
- Periodontal disease is a dystrophic disease of the gums.
- Stomatitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity.
Patients are predominantly referred to a periodontist by a general dentist after examination and initial diagnosis.
What kind of complaints to see a periodontist for
A dentist may refer a person with the following symptoms to a periodontist:
- bleeding gums;
- tartar;
- a discharge of pus from under the edge of the gum;
- increased sensitivity and exposure of the neck of the teeth;
- pain in the gum area;
- The appearance of tooth mobility and increased gaps between teeth.
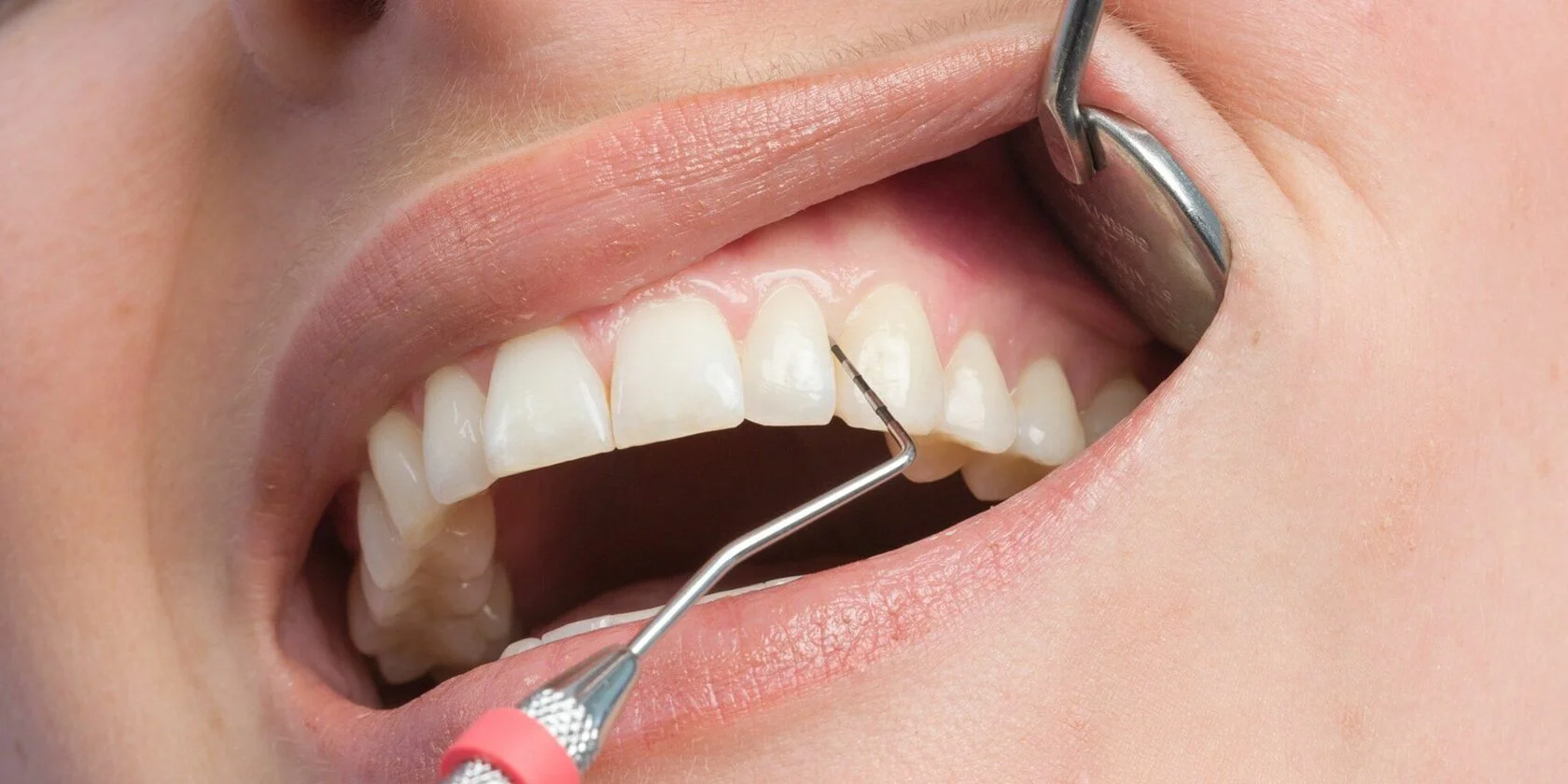
But complaints alone are not enough to make a diagnosis. Therefore, during the appointment, the periodontist draws up a periodontal chart, where he indicates the status of each tooth. As an additional method of examination, a CT scan is most often used, which gives a complete picture of the degree of disease development.
Treatment methods in periodontology
After examination and diagnosis, the periodontist determines the tactics of treatment, which in each case is selected individually. If necessary, the doctor performs stone removal, cleaning of gum pockets, as well as normalization of the gum margin. If the teeth are wobbly, splinting is performed to unite them into one whole.
In particularly advanced cases, surgical treatment for periodontal disease is performed. This includes bone grafting, gingivectomy, and curettage. If tooth loss is unavoidable, prosthetics or dental implants are performed. To prevent such serious pathologies, it is necessary to consult a doctor in time, as well as carefully monitor oral hygiene.
Sign up
Make an appointment with a gnathologist and get a personalized treatment plan
Read also
Contact us
Send a message
Please fill out the form below so we can provide a fast and efficient service
Contact by phone
-
Branch 1
-
Branch 2
-
Branch 3
-
Branch 4